Describe the Anatomy of a Neuron
This week as you begin to study psychopharmacology you will explore the basic functional unit of the nervous system the neuron. A cell body and nerve processes.
Describe the anatomy of the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron.
. Pay for the order. Also known as a soma the cell body is the core section of the neuron. Transmitting information throughout the body.
A neuron that is the basic unit of the nervous system is a nerve cell responsible for transmitting information to muscles glands and other nerve cells. You fill all the paper instructions in the order form. Integrate incoming signals to determine whether or not the information should be passed along.
Communicate signals to target cells other neurons or muscles or glands. Dendritic synapses create the terminals of axons and other dendrites in neurons and other neural structures. They are electrically active and release chemical signals to target cells.
Neuron is made up of three parts namely. In either case neurons propagate signals along their axons in the form of action potentials which. State the functions of a multipolar neuron.
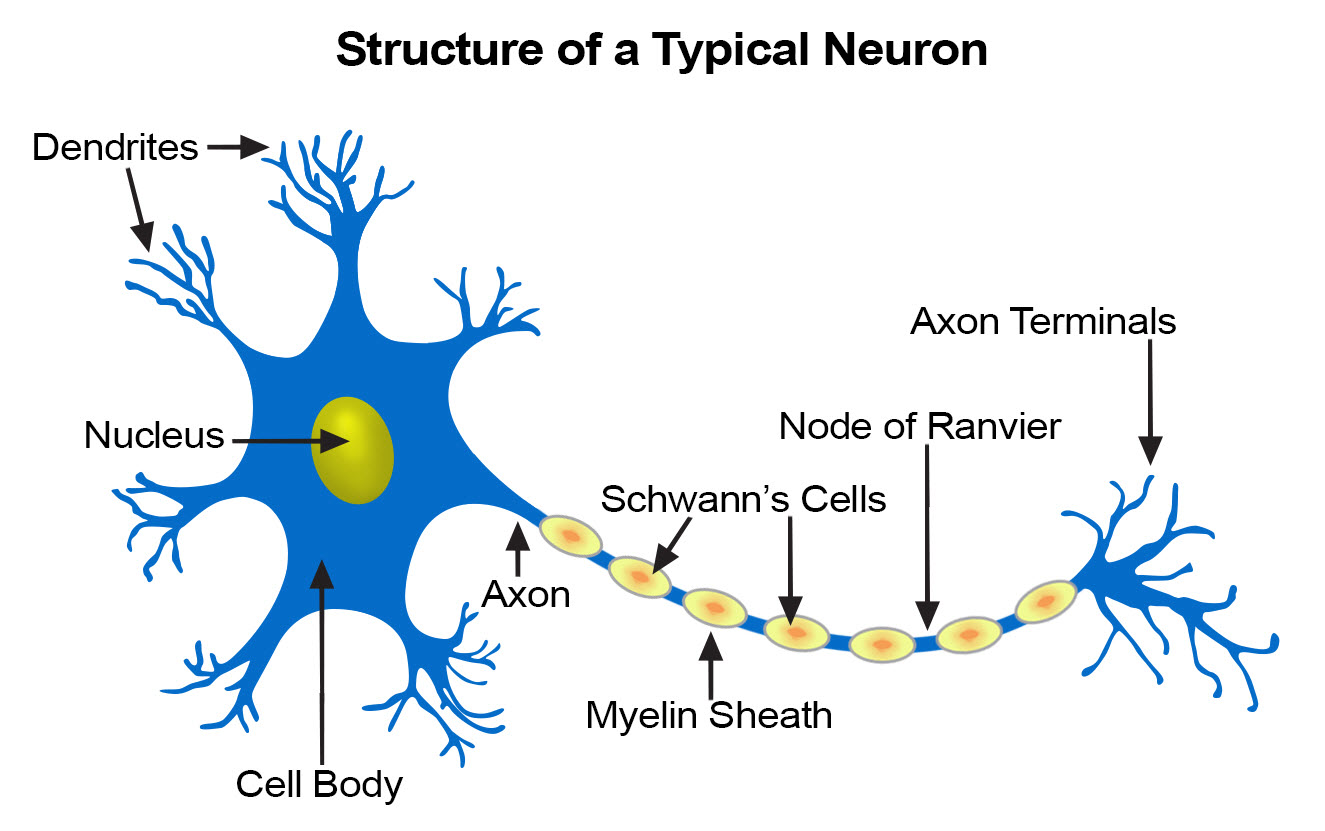
Synapse myelin sheath axon soma nucleus and dendrites. There are 3 types of neurons such as Sensory neurons motor neurons and InterneuronsA neuron has a cell body which includes the cell nucleus and a special extensions called Axons and dendrites. The basic unit of the nervous system is the neuron it is a cell in the nervous system whose function is to receive and transmit information.
How our Assignment Help Service Works. In 4 or 5 sentences describe the anatomy of the basic unit of the nervous system the neuron. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell.
The basic functions of a neuron. Neurons are a type of cells in our body that are incredibly specialized on a morphological level. Receive signals or information.
In sensory neurons however environmental stimuli light chemicals pain activate ion channels which produce action potentials that flow from the axon to the soma. A typical neuron consists of a cell body and neuronal processes such as dendrites and axon. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Describe the gross anatomy of spinal nerves and specify their location relative to the anatomy of. Start studying Anatomy of a Neuron and Types of Neurons. The neuron contains the soma cell body from which extend the axon a nerve fiber conducting electrical impulses away from the soma and dendrites tree-like structures that receive signals from other neurons.
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells neurons and glial cells. Neurons are cells within the nervous system that transmit information to other nerve cells muscle or gland cells. The cell body contains genetic information maintains the neurons structure and.
Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal. The cell body or the soma which contains the nucleus of the cell the dendrites which collects information from other cell and send the information to the soma and the axon whose function is transmit. The central cell body is the process part of a neuron and contains the neurons nucleus associated cytoplasm organelles and other cell structures.
Each neuron has a cell body with a nucleus Golgi body endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria and other components. The neuron is the basic working unit of the brain a specialized cell designed to transmit information to other nerve cells muscle or gland cells. Make sure you include all the helpful materials so that our academic writers.
Anatomy of a Neuron. A number of anatomically distinct neuron types such as sensory motor and interneurons have evolved to participate in different organismal functions. Pay for the order.
How our Assignment Help Service Works. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. One of the cell bodys smaller axonal branches emerges and ends at the nerve terminal.
Neurons contain the same cellular components as other body cells. Define the term nerve i. You fill all the paper instructions in the order form.
Neurons are responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body a process that allows us to move and exist in the world around us. A neurons dendrites and axons are two of its three components. Anatomy of the spinal nerves a.
Dendrites are extensions leading toward cell body that receives signal from other neurons and send them to the cell body. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. Neurons are the cells that transmit nerve impulses between parts of the nervous system.
Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The cell body produces proteins needed for the construction of other. Anatomy of the Neuron.
A neuron has six major parts. A neuron consists of two major parts. Include each part of the neuron and a general overview of electrical impulse conduction the pathway it travels and the net result at the termination of the impulse.
Different types of neurons include sensory motor and interneurons as well as structurally-based neurons which include unipolar multipolar bipolar and pseudo-unipolar neurons. Describe how neurons in a nerve are packaged. The cell body is made up of the nucleus and cytoplasm.
You will review the structure of the neuron and you will examine the anatomy of the central nervous system and consider the functionality of the different. From there the message can move to the next neuron. PHYSIOLOGY OF THE NEURON.
Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. A neuron is a specialized cell primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. Make sure you include all the helpful materials so that our academic writers.
They are found in the brain spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Most neurons have a cell body an axon and dendrites. The basic unit of nervous system is a neuron.
Neurons can generally be anatomically characterized as unipolar bipolar or multipolar. And physiological in fulfilling an essential function. Typically voltage changes in neurons flow from dendrites to the soma to the axon.
Axon is a tube-like structure that carries electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals that passes the impulse to another neuron. The structure of a neuron varies with their shape and size and it mainly depends upon their functions and their.
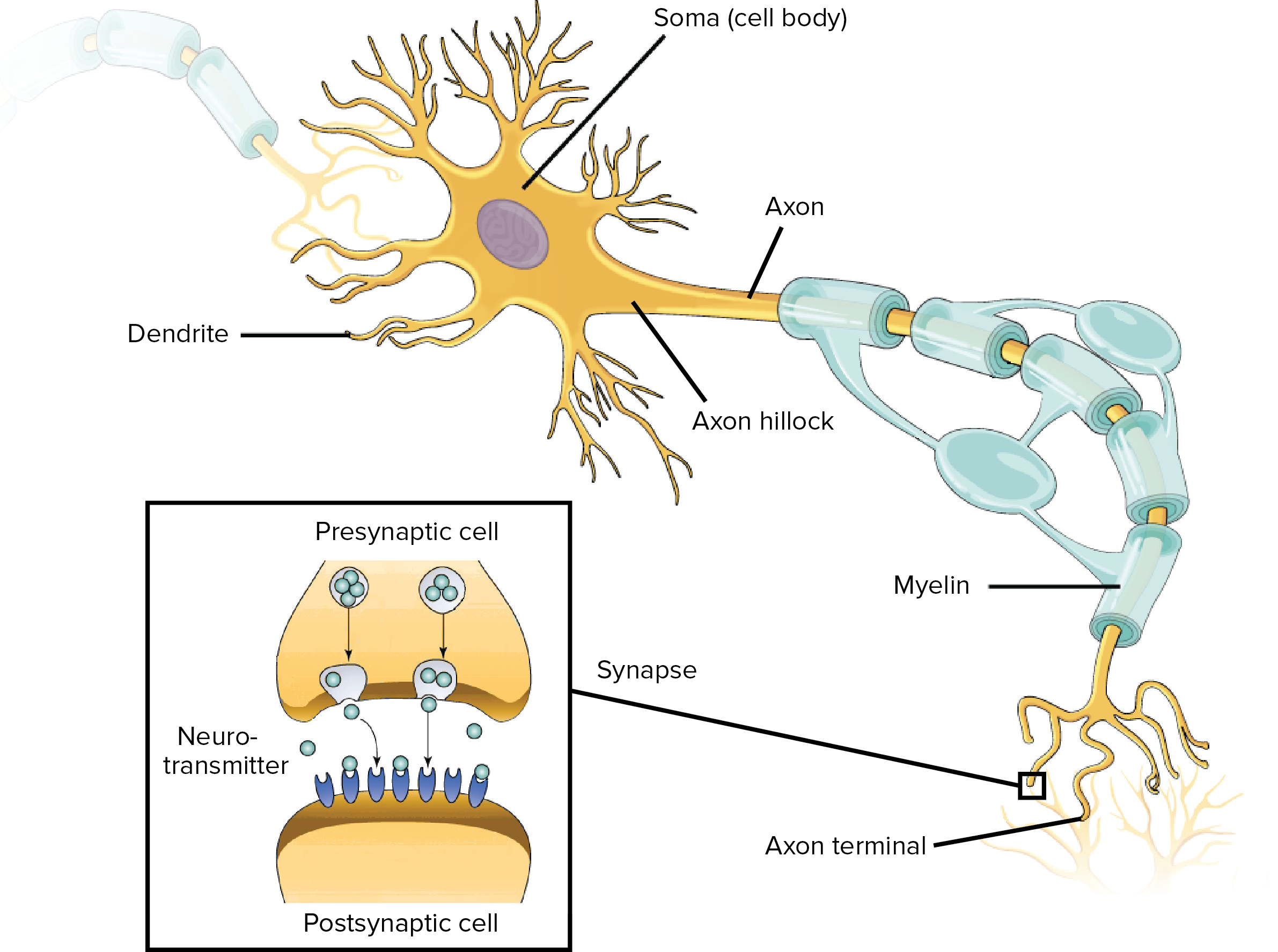
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
Overview Of Neuron Structure And Function Article Khan Academy
4 1 The Neuron Is The Building Block Of The Nervous System Introduction To Psychology 1st Canadian Edition

Comments
Post a Comment